Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Cladus: Sarcopterygii
Cladus: Rhipidistia
Cladus: Tetrapodomorpha
Cladus: Eotetrapodiformes
Cladus: Elpistostegalia
Superclassis: Tetrapoda
Cladus: Reptiliomorpha
Cladus: Amniota
Cladus: Synapsida
Cladus: Eupelycosauria
Cladus: Sphenacodontia
Cladus: Sphenacodontoidea
Cladus: Therapsida
Cladus: Theriodontia
Cladus: Cynodontia
Cladus: Eucynodontia
Cladus: Probainognathia
Cladus: Prozostrodontia
Cladus: Mammaliaformes
Classis: Mammalia
Subclassis: Trechnotheria
Infraclassis: Zatheria
Supercohors: Theria
Cohors: Eutheria
Infraclassis: Placentalia
Cladus: Boreoeutheria
Superordo: Euarchontoglires
Ordo: Rodentiaa
Subordo: Sciuromorpha
Familia: Sciuridae
Subfamilia: Sciurinae
Tribus: Pteromyini
Genus: Petaurista
Species: Petaurista leucogenys
Subspecies: P. l. hintoni – P. l. leucogenys – P. l. nikkonsis – P. l. oreas
Name
Petaurista leucogenys (Temminck, 1827)
References
Petaurista leucogenys in Mammal Species of the World.
Wilson, Don E. & Reeder, DeeAnn M. (Editors) 2005. Mammal Species of the World – A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. Third edition. ISBN 0-8018-8221-4.
IUCN: Petaurista leucogenys (Temminck, 1827) (Least Concern)
Vernacular names
Deutsch: Japanisches Riesengleithörnchen
English: Japanese giant flying squirrel
日本語: ムササビ
Nederlands: Witkelige vliegende eekhoorn
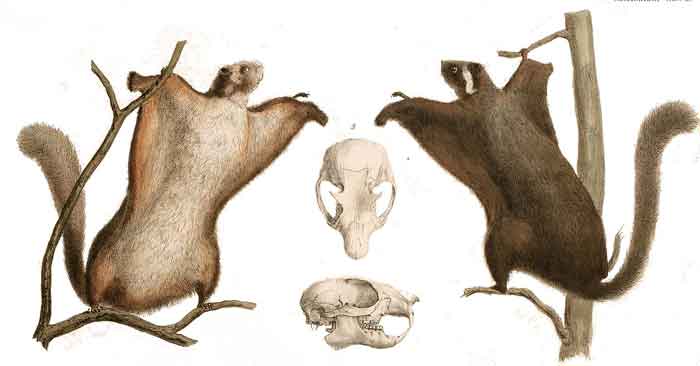
The Japanese giant flying squirrel (ムササビ, musasabi, Petaurista leucogenys) is a species of flying squirrel, one of the giant flying squirrels in the genus Petaurista.
Description
Like other flying squirrels, it has a web of skin between its legs which it uses to glide between trees. Glides of 160 metres have been recorded. The tail is used for stability during flight. The body is about 25–50 cm long, and the tail a further 30–40 cm. It weighs between 700 and 1500g. It is much larger than the related Japanese dwarf flying squirrel which does not exceed 220g. It eats fruit and nuts and lives in holes in large trees. The female has a home range of about a hectare and the male about two hectares.
Distribution and habitat
It is native to Japan, where it inhabits sub-alpine forests and boreal evergreen forests on the islands of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu.
Reproduction
Sexual maturity is reached after about two years.[2] From winter to early summer the males compete for females. During mating, after ejaculation, the male produces a sticky protein called a coitus plug from his penis which becomes firm and blocks the female's vagina. This may stop semen from leaking out and heighten the chances of fertilization. It also prevents other males from mating with the same female. However males can use their penis to remove the coitus plug. Gestation lasts about 74 days and one or two young are born in early autumn.[3]
References
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Petaurista leucogenys.
Wikispecies has information related to Petaurista leucogenys.
Ishii, N. & Kaneko, Y. (2008). "Petaurista leucogenys". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. Retrieved 6 January 2009.
Kawamichi, Takeo. "The age of sexual maturity in Japanese giant flying squirrels, Petaurista leucogenys." Mammal Study 22.1+ 2 (1997): 81-87.
Kawamichi, Takeo. "Biannual reproductive cycles in the Japanese giant flying squirrel (Petaurista leucogenys)." Journal of Mammalogy 91.4 (2010): 905-913.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

