|
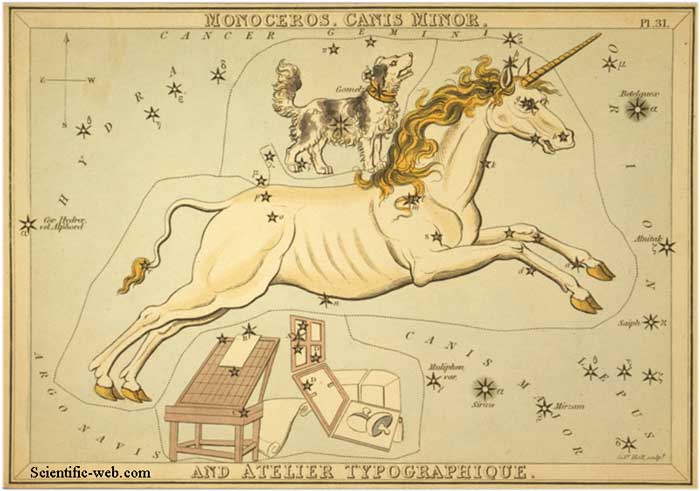
Canis Minor ( Latin: smaller dog) is one of the 88 modern constellations, and was also in Ptolemy's list of 48 constellations. It is said to represent one of the dogs following Orion the hunter. Notable features Canis Minor is a small constellation mainly consisting of the two stars, Procyon (α CMi, 0.38m) and Gomeisa (β CMi , 2.9m). Procyon is the eighth brightest star in the night sky. Procyon means "before the dog" in Greek, as it rises an hour before the Dog Star, Sirius, of Canis Major, the large dog. Notable deep objects Being such a small constellation, Canis Minor has no deep sky object brighter than magnitude 15. Mythology Canis Minor was considered to be the smaller of the two hunting dogs of Orion. However, the ancient Greeks did not recognise it as a distinct constellation, and thus originally only considered Orion to have had one dog. See also the constellations of Orion and Canis Major Canis Minor is also connected with the Teumessian Fox, beast turned into stone with its hunter, Laelaps, by Zeus, who placed them in heaven as Canis Mayor (Laelaps) and Canis Minor (Teumessian Fox). See also * Orion * Procyon
Monoceros, Canis Minor, and Atelier Typographique References * Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide Links
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||