Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Cladus: Sarcopterygii
Cladus: Rhipidistia
Cladus: Tetrapodomorpha
Cladus: Eotetrapodiformes
Cladus: Elpistostegalia
Superclassis: Tetrapoda
Cladus: Reptiliomorpha
Cladus: Amniota
Classis: Reptilia
Cladus: Eureptilia
Cladus: Romeriida
Subclassis: Diapsida
Cladus: Sauria
Infraclassis: Archosauromorpha
Cladus: Crurotarsi
Divisio: Archosauria
Cladus: Avemetatarsalia
Cladus: Ornithodira
Subtaxon: Dinosauromorpha
Cladus: Dinosauriformes
Cladus: Dracohors
Cladus: Dinosauria
Ordo: Saurischia
Cladus: Eusaurischia
Cladus: Theropoda
Cladus: Neotheropoda
Cladus: Averostra
Cladus: Tetanurae
Cladus: Avetheropoda
Cladus: Coelurosauria
Cladus: Tyrannoraptora
Cladus: Maniraptoromorpha
Cladus: Maniraptoriformes
Cladus: Maniraptora
Cladus: Pennaraptora
Cladus: Paraves
Cladus: Eumaniraptora
Cladus: Avialae
Infraclassis: Aves
Cladus: Euavialae
Cladus: Avebrevicauda
Cladus: Pygostylia
Cladus: Ornithothoraces
Cladus: Ornithuromorpha
Cladus: Carinatae
Parvclassis: Neornithes
Cohors: Neognathae
Cladus: Neoaves
Cladus: Aequornithes
Ordo: Suliformes
Familia: Sulidae
Genus: Sula
Species: S. dactylatra – S. granti – S. leucogaster – S. nebouxii – S. sula – S. variegata
Name
Sula Brisson, 1760
Typus
Pelecanus leucogaster Boddaert, 1783 = Sula leucogaster
References
Brisson, M.J. 1760. Ornithologie ou méthode contenant la division des oiseaux en ordres, sections, genres, especes & leurs variétés. A laquelle on a joint une description exacte de chaque espece, avec les citations des auteurs qui en ont traité, les noms qu'ils leur ont donnés, ceux que leur ont donnés les différentes nations, & les noms vulgaires. Ouvrage enrichi de figures en taille-douce. Tome I. - pp. j-xxiv [= 1-24], 1-526, j-lxxiij [= 1-73], Pl. I-XXXVII [= 1-37]. Paris. (Bauche). Original description p.60 BHL Reference page. Tome 6 p.494 BHL
Vernacular names
مصرى: اخبل
العربية: أخبل
English: Booby
Esperanto: Sulo
español: Piquero
فارسی: بوبی
suomi: Ruskosuulat
Gaeilge: Búbaí
עברית: סולה
հայերեն: Խոլահավեր
Bahasa Indonesia: Angsa-batu
italiano: Sule
日本語: カツオドリ属
한국어: 얼가니새
മലയാളം: ബൂബി
پنجابی: بوبی
português do Brasil: Atobás
português: Alcatraz
русский: Олуши
slovenščina: Tropski strmoglavci
Kiswahili: Ndegejinga
தமிழ்: பூபி
ไทย: นกบูบี
lea faka-Tonga: Ngutulei
українська: Сула
Tiếng Việt: Chim điên
中文: 鲣鸟属
A booby is a seabird in the genus Sula, part of the family Sulidae. Boobies are closely related to the gannets (Morus), which were formerly included in Sula.
Systematics and evolution
The genus Sula was introduced by the French zoologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson in 1760.[3] The type species is the brown booby.[4] The name is derived from súla, the Old Norse and Icelandic word for the other member of the family Sulidae, the gannet.[5]
The English name "booby" was possibly based on the Spanish slang term bobo, meaning "stupid",[6] as these tame birds had a habit of landing on board sailing ships, where they were easily captured and eaten. Owing to this, boobies are often mentioned as having been caught and eaten by shipwrecked sailors, notably William Bligh of the Bounty and his adherents during their famous voyage after being set adrift by Fletcher Christian and his followers.
Six of the ten extant Sulidae species called boobies are in the genus Sula, while the three gannet species are usually placed in the genus Morus.[7] Abbott's booby was formerly included in Sula but is now placed in a monotypic genus Papasula, which represents an ancient lineage perhaps closer to Morus.
Some authorities consider that all ten species should be considered congeneric in Sula. However, they are readily distinguished by means of osteology. The distinct lineages of gannets and boobies are known to have existed in such form, since at least the Middle Miocene, c. 15 mya.[8]
The fossil record of boobies is not as well documented as that of gannets, either because booby speciation was lower from the late Miocene to the Pliocene (when gannet diversity was at its highest), or because the booby fossil species record is as yet incomplete, due to most localities being in continental North America or Europe despite boobies' more tropical distribution.
Behaviour
See also: Seabird breeding behavior § Mating dances
Boobies hunt fish by diving from a height into the sea and pursuing their prey underwater. Facial air sacs under their skin cushion the impact with the water. Boobies are colonial breeders on islands and coasts. They normally lay one or more chalky-blue eggs on the ground or sometimes in a tree nest. Selective pressures, likely through competition for resource, have shaped the ecomorphology and foraging behaviours of the six species of boobies in the Pacific.[9]
List of species
| Common name | Scientific name | IUCN Red List Status | Distribution | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue-footed booby | Sula nebouxii Milne-Edwards, 1882 |
LC IUCN[10] | _world2.png/180px-Blaufußtoelpel_(Sula_nebouxii)_world2.png) |
 |
| Brown booby | Sula leucogaster (Boddaert, 1783) |
LC IUCN[11] |  |
 |
| Masked booby | Sula dactylatra Lesson, 1831 |
LC IUCN[12] |  |
 |
| Nazca booby | Sula granti Rothschild, 1902 |
LC IUCN[13] |  |
 |
| Peruvian booby | Sula variegata (Tschudi, 1843) |
LC IUCN[14] |  |
 |
| Red-footed booby | Sula sula (Linnaeus, 1766) |
LC IUCN[15] | 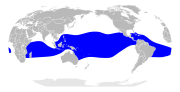 |
 |
References
"Sula Brisson 1760 (booby)". PBDB. Archived from the original on 2021-08-08. Retrieved 2019-07-08.
Patterson, S.A.; Morris-Pocock, J.A.; Friesen, V.L (2011). "A multilocus phylogeny of the Sulidae (Aves: Pelecaniformes)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 58 (2): 181–191. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.11.021. PMID 21144905.
Brisson, Mathurin Jacques (1760). Ornithologie, ou, Méthode contenant la division des oiseaux en ordres, sections, genres, especes & leurs variétés (in French and Latin). Vol. 1. Paris: Jean-Baptiste Bauche. Vol. 1 p. 60, Vol. 6 p.494.
Mayr, Ernst; Cottrell, G. William, eds. (1979). Check-list of Birds of the World. Vol. 1 (2nd ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Museum of Comparative Zoology. p. 181. Archived from the original on 2021-08-08. Retrieved 2017-11-21.
"Sula, n.". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
"booby, n.". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
Friesen, V. L.; Anderson, D. J.; Steeves, T.E.; Jones, H.; Schreiber, E.A. (2002). "Molecular support for species status of the Nazca Booby". The Auk. 119 (3): 820–826. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2002)119[0820:MSFSSO]2.0.CO;2.
Olson, Storrs L. "The Fossil Record of Birds (Section X.G.5.a Sulidae)". In Farner, D.S.; King, D.S.; Parkes, K.C. (eds.). Avian Biology. Vol. 8. New York: Academic Press. pp. 79–238 [203–204]. hdl:10088/6553. Archived from the original on 2021-04-10. Retrieved 2017-11-22.
van Oordt, F.; Torres-Mura, J. C.; Hertel, F. (2018). "Ecomorphology and foraging behaviour of Pacific boobies". Ibis. 160 (2): 313–326. doi:10.1111/ibi.12545.
BirdLife International (2018). "Sula nebouxii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22696683A132588719. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22696683A132588719.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
BirdLife International (2018). "Sula leucogaster". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22696698A132590197. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22696698A132590197.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
BirdLife International (2018). "Sula dactylatra". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22736173A132666363. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22736173A132666363.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
BirdLife International (2018). "Sula granti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22728990A132659882. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22728990A132659882.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
BirdLife International (2018). "Sula variegata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22696686A132589026. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22696686A132589026.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
BirdLife International (2018). "Sula sula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22696694A132589278. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22696694A132589278.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

