Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Cladus: Sarcopterygii
Cladus: Rhipidistia
Cladus: Tetrapodomorpha
Cladus: Eotetrapodiformes
Cladus: Elpistostegalia
Superclassis: Tetrapoda
Cladus: Reptiliomorpha
Cladus: Amniota
Classis: Reptilia
Cladus: Eureptilia
Cladus: Romeriida
Subclassis: Diapsida
Cladus: Sauria
Infraclassis: Archosauromorpha
Cladus: Crurotarsi
Divisio: Archosauria
Cladus: Avemetatarsalia
Cladus: Ornithodira
Subtaxon: Dinosauromorpha
Cladus: Dinosauriformes
Cladus: Dracohors
Cladus: Dinosauria
Cladus: Saurischia
Cladus: Eusaurischia
Subordo: Theropoda
Cladus: Neotheropoda
Cladus: Averostra
Cladus: Tetanurae
Cladus: Avetheropoda
Cladus: Coelurosauria
Cladus: Tyrannoraptora
Cladus: Maniraptoromorpha
Cladus: Maniraptoriformes
Cladus: Maniraptora
Cladus: Pennaraptora
Cladus: Paraves
Cladus: Eumaniraptora
Cladus: Avialae
Infraclassis: Aves
Cladus: Avebrevicauda
Cladus: Pygostylia
Cladus: Ornithothoraces
Cladus: Ornithuromorpha
Cladus: Carinatae
Parvclassis: Neornithes
Cohors: Neognathae
Cladus: Neoaves
Cladus: Telluraves
Cladus: Australaves
Ordo: Passeriformes
Subordo: Passeri
Infraordo: Passerida
Superfamilia: Passeroidea
Familia: Icteridae
Genus: Psarocolius
Species: Psarocolius bifasciatus
Subspecies: P. b. bifasciatus – P. b. neivae – P. b. yuracares
Name
Psarocolius bifasciatus (Spix, 1824)
Type locality: 'in sylvis prope Maranhao et Param'; restricted to environs of Belém, Pará, Brazil.
Synonyms
Cassicus bifasciatus (protonym)
Gymnostinops bifasciatus (Spix, 1824)
References
Primary references
Spix, J.B. von 1824. Avium species novae, quas in itinere per Brasiliam annis MDCCCXVII-MDCCCXX jussu et auspiciis Maximiliani Josephi I. Bavariae regis augustissimi. Suscepto. Collegit et descripsit Dr. Joannes Bapt. de Spix. Curavit Martius, C.F.P. von. 1: 90 pp. + 104 tt. Illustrations: Matthias Schmidt. Ed. Monachii, Impensis Editoris, 1838. DOI: 10.5962/bhl.title.63181 p. 65 BHL Reference page. pl. 61 BHL
Additional references
Price, J.J. & Lanyon, S.M. 2002. A robust phylogeny of the oropendolas: polyphyly revealed by mitochondrial sequence data. Auk 119: 335–348 pdf DOI: 10.1093/auk/119.2.335 Open access Reference page.
Vernacular names
English: Amazonian Oropendola
español: Cacique de Pará
português: Japuaçu
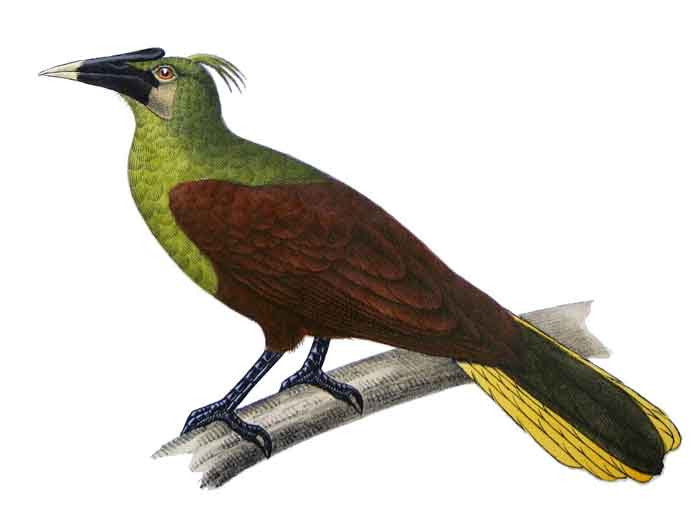
The olive oropendola (Psarocolius bifasciatus) is the largest member of the icterid family and rivals the Amazonian umbrellabird as the largest passerine bird in South America. It is sometimes placed in the genus Gymnostinops instead of Psarocolius. As suggested by its name, it is found widely – but often in low densities – throughout humid lowland forests of the Amazon Basin, with the notable exception of most of the Guiana Shield. It is sometimes split into two species, the western olive oropendola (P. yuracares) and the eastern Pará oropendola (P. bifasciatus), but the subspecies P. y. neivae is widely recognized as a hybrid swarm, and the vast majority of authorities consider them a single species.
Description
The sexes of this icterid are very different in size: the male is 52 cm (21 in) long and weighs 550 g (1.2 lbs); the smaller female is 41 cm (16 in) long and weighs 260 g (9.2 oz). Confusingly, the name "olive oropendola" is usually used for this combined species, despite the fact that the nominate subspecies has no olive to its plumage, as its head and chest are black (these are olive in P. b. yuracares). The back, wings and belly of this large oropendola are brown, the outer rectrices are yellow (i.e. tail appears all yellow from below), the bare facial skin is pink, the eyes are brown, and the bill is black with an orange tip. The superficially similar green oropendola has an olive back and wing-coverts, lacks extensive bare facial-skin, has a pale bill with an orange tip, and blue eyes.
Behavior
The olive oropendola is a canopy bird that most often is seen flying high over the tops of the trees. Compared to other oropendolas it is a "loner" most frequently seen alone or in pairs, and drawing less attention to itself than its cousins, despite the greater size. Small groups are seen occasionally, and may even mix with other oropendolas. The breeding colonies are small, usually with fewer than five birds. The nest is a hanging woven ball fibers and vines, 60–180 cm long, high in a tree. Relatively little is known about these bird's breeding habits.
The omnivorous diet appears to be fairly catholic. They may eat small vertebrates (especially amphibians and reptiles), large insects, nectar, and fruit. They often travel great distances through the forests, except when lingering around their nesting colony.
The song of the olive oropendola is a liquid, gurgling and "expanding" stek-ek-ek-ek-eh-eh-eh-o'o 'GLOOP!, given as a displaying male falls forward on a perch and rustles his wings over the back. Nasal raap and whrup calls are given while in flight or when foraging.
References
BirdLife International (2017). "Psarocolius bifasciatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T103780801A119474723. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T103780801A119474723.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
Hilty, Steven L. (2003): Birds of Venezuela. Christopher Helm, London. ISBN 0-7136-6418-5
Olive Oropendola (Psarocolius bifasciatus yuracares) arthurgrosset.com. Retrieved on 15 January 2009.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

