Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Cladus: Sarcopterygii
Cladus: Rhipidistia
Cladus: Tetrapodomorpha
Cladus: Eotetrapodiformes
Cladus: Elpistostegalia
Superclassis: Tetrapoda
Cladus: Reptiliomorpha
Cladus: Amniota
Classis: Reptilia
Cladus: Eureptilia
Cladus: Romeriida
Subclassis: Diapsida
Cladus: Sauria
Infraclassis: Archosauromorpha
Cladus: Crurotarsi
Divisio: Archosauria
Cladus: Avemetatarsalia
Cladus: Ornithodira
Subtaxon: Dinosauromorpha
Cladus: Dinosauriformes
Cladus: Dracohors
Cladus: Dinosauria
Cladus: Saurischia
Cladus: Eusaurischia
Subordo: Theropoda
Cladus: Neotheropoda
Cladus: Averostra
Cladus: Tetanurae
Cladus: Avetheropoda
Cladus: Coelurosauria
Cladus: Tyrannoraptora
Cladus: Maniraptoromorpha
Cladus: Maniraptoriformes
Cladus: Maniraptora
Cladus: Pennaraptora
Cladus: Paraves
Cladus: Eumaniraptora
Cladus: Avialae
Infraclassis: Aves
Cladus: Avebrevicauda
Cladus: Pygostylia
Cladus: Ornithothoraces
Cladus: Ornithuromorpha
Cladus: Carinatae
Parvclassis: Neornithes
Cohors: Neognathae
Cladus: Neoaves
Cladus: Telluraves
Cladus: Australaves
Ordo: Passeriformes
Subordo: Passeri
Infraordo: Passerida
Superfamilia: Passeroidea
Familia: Estrildidae
Genus: Mandingoa
Species: Mandingoa nitidula
Subspecies (4): M. n. chubbi – M. n. nitidula – M. n. schlegeli – M. n. virginiae
Name
Mandingoa nitidula (Hartlaub, 1865)
Vernacular names
ReferencesIbis p. 269
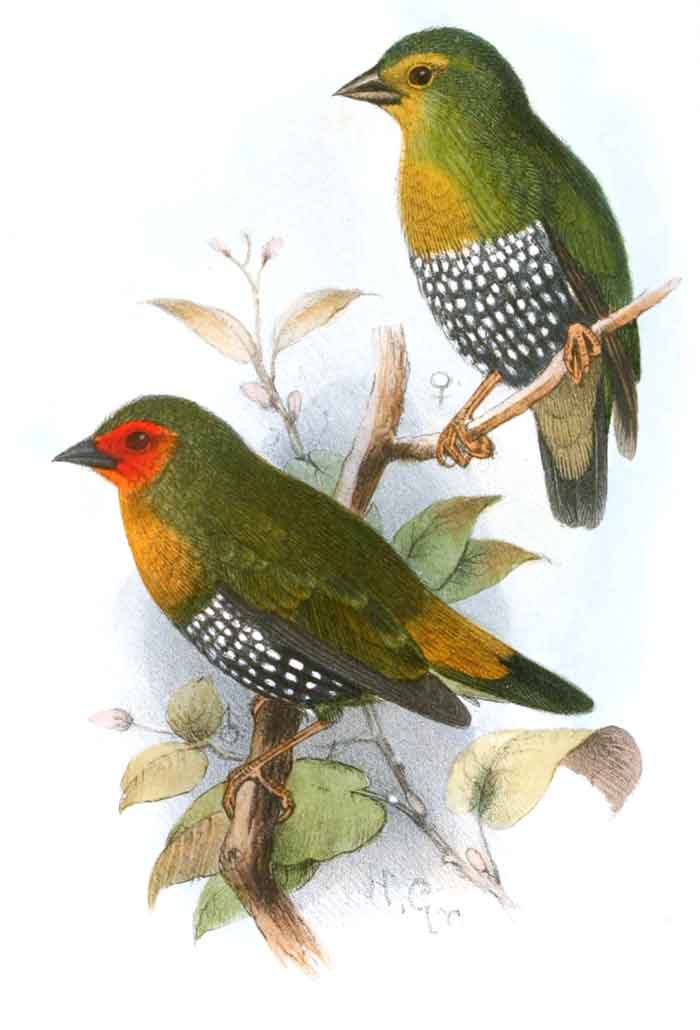
The green-backed twinspot or green twinspot (Mandingoa nitidula) is an estrildid finch found in many parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. The IUCN has classified the species as being of least concern.
Subspecies
The green-backed twinspot has four sub-species:
Mandingoa nitidula chubbi
Mandingoa nitidula nitidula
Mandingoa nitidula schlegeli
Mandingoa nitidula virginiae
Habitat
The green-backed twinspot inhabits lowland moist forests of the tropical region. It may also be found in grassland and shrubland habitats.
Males are distinguished from females by their bright red facial feathers. Females have an olive-green face and darker (almost black) beak.
Aviculture
Green-backed twinspot in Budongo Forest, Uganda
The green backed twinspot prefers its privacy in regards to breeding. Males in the breeding season will raise their heads, looking straight up while "dancing" on the perch next to the female, moving in a side-stepping fashion. The female, if receptive, will crouch down and point her tail to the male. Green backed twinspots tend to pair with one female and care for her and the young while breeding. Up to four eggs are laid about five days after mating, usually one daily. The female will go in and out of the nest frequently until all eggs are laid and will sit in place to incubate thereafter, ensuring all hatch in relatively close proximity.
This species enjoys a large, planted aviary with plenty of privacy for breeding. Temperatures in captivity should not dip below 70 °F or exceed 84 °F. Green back twinspots may be housed as single pairs, singles, or in groups up to four pairs in a large flight.
The birds eat millet, dark leafy greens, fresh bananas, cooked brown rice and mixed finch seed.
References
BirdLife International (2018). "Mandingoa nitidula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22719354A132127786. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22719354A132127786.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
External links
Avibase Archived 2007-09-30 at the Wayback Machine
BirdLife International species factsheet
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

