Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Otomorpha
Subcohors: Ostariophysi
Sectio: Otophysa
Ordo: Siluriformes
Familia: Amphiliidae
Subfamilia: Doumeinae
Genus: Phractura
Species: P. ansorgei – P. ansorgii – P. bovei – P. brevicauda – P. clauseni – P. fasciata – P. gladysae – P. ineac – P. intermedia – P. lindica – P. longicauda – P. lukugae – P. macrura – P. scaphyrhynchura – P. tenuicauda
Name
Phractura Boulenger, 1900
References
FishBase
Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS)
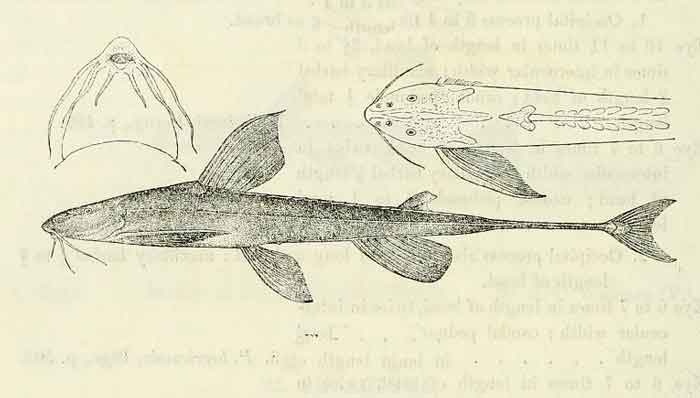
Phractura bovei
Phractura is a genus of loach catfishes (order Siluriformes) that occur in Africa.
Phractura species are elongated fish with a long caudal peduncle and bony scutes on the sides, back, and belly.,[1] this feature giving the genus its name from the Greek phraktos, which means enclosed and oura which means tail.[2] Phractura species are often associated with vegetation.[1] The genus was originally given the name Peltura but this name was preoccupied by a genus of trilobites which the name Peltura had been applied to by Louis Agassiz in 1846.[3] Phractura species, like other genera in Doumeinae, have a mouth modified into a suckermouth that allows it to clean to the objects and scrape the surface of the substrate.[4]
Species
There are currently 13 recognized species in this genus:[5]
Phractura ansorgii Boulenger, 1902 (African whiptailed catfish)
Phractura bovei Perugia, 1892
Phractura brevicauda Boulenger, 1911
Phractura clauseni Daget & Stauch, 1963
Phractura fasciata Boulenger, 1920
Phractura gladysae Pellegrin, 1931
Phractura intermedia Boulenger, 1911
Phractura lindica Boulenger, 1902
Phractura longicauda Boulenger, 1903
Phractura macrura Poll, 1967
Phractura scaphyrhynchura Vaillant, 1886
Phractura stiassny Skelton, 2007[6]
Phractura tenuicauda Boulenger, 1902
References
Skelton, Paul H. (1992). "Amphiliidae" (PDF). Faune des poissons d'eaux douces et saumâtres d'Afrique de l'Ouest (in French). Vol. Tome 2. Musée Royal de l'Afrique Centrale, Tervuren, Belgique and O.R.S.T.O.M., Paris, France, 902. pp. 450–467.
"Summary of Phractura". PlabetCatish.com. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
Carl J. Ferraris Jr. (2007). "Checklist of catfishes, recent and fossil (Osteichthyes: Siluriformes), and catalogue of siluriform primary types" (PDF). Zootaxa. 1418: 1–625. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1418.1.1.
Diogo, Rui; Oliveira, Claudia; Chardon, Michel (January 2000). "On the anatomy and function of the cephalic structures in Phractura (Siluriformes: Amphiliidae), with comments on some striking homoplasies occurring between the Doumeinae and some loricaroid catfishes" (PDF). Belg. J. Zool. 130 (1): 117–130.
Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2011). Species of Phractura in FishBase. December 2011 version.
Skelton, Paul H. (2007). "New species of the amphiliid catfish genera Amphilius, Doumea and Phractura and the taxonomy of Paramphilius from West Central Africa (Siluriformes, Amphiliidae)" (PDF). Zootaxa. 1578: 41–68. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1578.1.2.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

