Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Euteleosteomorpha
Subcohors: Neoteleostei
Infracohors: Eurypterygia
Sectio: Ctenosquamata
Subsectio: Acanthomorphata
Divisio/Superordo: Acanthopterygii
Subdivisio: Percomorphaceae
Series: Eupercaria
Ordo: Lophiiformes
Subordo: Lophioidei
Familia: Lophiidae
Genus: Lophiodes
Species: L. beroe – L. bruchius – L. caulinaris – L. endoi – L. fimbriatus – L. gracilimanus – L. insidiator – L. iwamotoi – L. kempi – L. lugubris – L. maculatus – L. miacanthus – L. monodi – L. mutilus – L. naresi – L. reticulatus – L. spilurus – L. triradiatus
Name
Lophiodes Goode & Bean, 1896
Gender: masculine
Type species: Lophius mutilus Alcock, 1894, by monotypy.
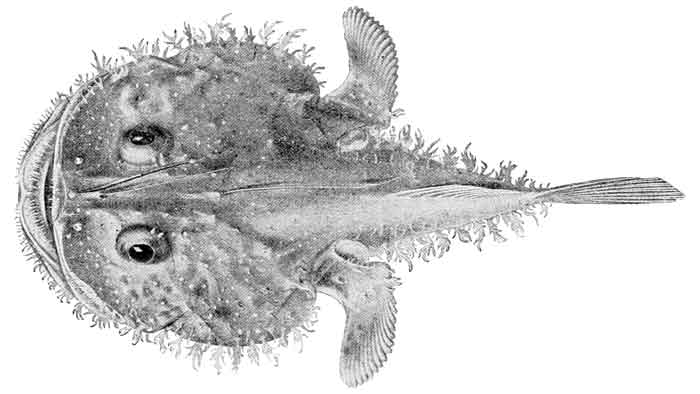
Lophiodes miacanthus
References
Goode, G. B. & T. H. Bean (1896) Oceanic ichthyology, a treatise on the deep-sea and pelagic fishes of the world, based chiefly upon the collections made by the steamers Blake, Albatross, and Fish Hawk in the northwestern Atlantic, with an atlas containing 417 figures. Special Bulletin U. S. National Museum No. 2: Text: i-xxxv + 1-26 + 1-553, Atlas: i-xxiii, 1-26, 123 pls.
Ho, H.-c.; Séret, B.; Shao, K.-t. 2009: Redescription of Lophiodes infrabrunneus Smith and Radcliffe, 1912, a senior synonym of L. abdituspinus Ni, Wu and Li, 1990 (Lophiiformes: Lophiidae). Zootaxa, 2326: 62–68. Abstract & excerpt PDF
Links
Lophiodes – Taxon details on Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS).
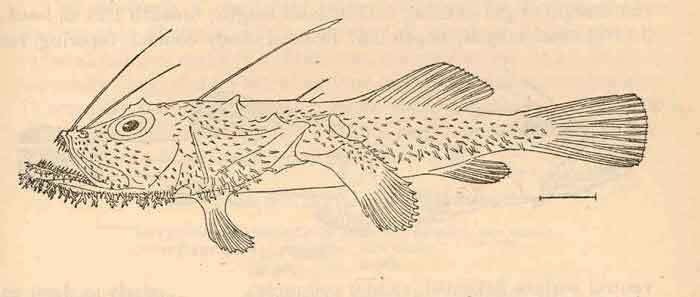
Lophiodes mutilus
Lophiodes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Lophiidae, the goosefishes, monkfishes and anglers. It is one of four extant genera in the family Lophiidae. The fish in this genus are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.
Taxonomy
Lophiodes was first proposed as a monospecific genus in 1896 by the American ichthyologists George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean with Lophius mutilis, a species described in 1894 by the English physician, naturalist and carcinologist Alfred William Alcock with its type locality given as the Bay of Bengal, as its only species.[1][2] The genus Lophiodes is one of 4 extant genera in the family Lophiidae which the 5th edition of Fishes of the World classifies in the monotypic suborder Lophioidei with the order Lophiiformes.[3] Within the Lophiidae, Lophiodes is the sister taxon to Lophius and Lophiomus with Sladenia as the most basal sister group to the other three genera.[4]
Etymology
Lophiodes means "having the form of Lophius, the type genus of the Lophiidae. Lophius means "mane" and is presumably a reference to the first 3spines of the first dorsal fin which are tentacle like, with 3 smaller spines behind them.[5]
Species
There are currently 18 recognized species in this genus:[6]
Lophiodes beroe J. H. Caruso, 1981 (White goosefish)
Lophiodes bruchius J. H. Caruso, 1981
Lophiodes caulinaris (Garman, 1899) (Spottedtail angler)
Lophiodes endoi H. C. Ho & K. T. Shao, 2008 [7]
Lophiodes fimbriatus Saruwatari & Mochizuki, 1985
Lophiodes gracilimanus (Alcock, 1899)
Lophiodes insidiator (Regan, 1921) (Natal angler)
Lophiodes iwamotoi H. C. Ho, Séret & K. T. Shao, 2011 (Long-spine angler) [8]
Lophiodes kempi (Norman, 1935) (Longspine African angler)
Lophiodes lugubris (Alcock, 1894)
Lophiodes maculatus H. C. Ho, Séret & K. T. Shao, 2011 (Spotted angler) [8]
Lophiodes miacanthus (C. H. Gilbert, 1905)
Lophiodes monodi Y. Le Danois, 1971 (Club-bait goosefish)
Lophiodes mutilus (Alcock, 1894) (Smooth angler)
Lophiodes naresi (Günther, 1880) (Goosefish)
Lophiodes reticulatus J. H. Caruso & Suttkus, 1979 (Reticulated goosefish)
Lophiodes spilurus (Garman, 1899) (Threadfin angler)
Lophiodes triradiatus (R. E. Lloyd, 1909) (Shortspine goosefish) [9]
Characteristics
Lophiodes goosefishes are characterised by having the head and the front part of the body flattened and wide, with the body becoming slenderer towards the tail. They have a pair of smooth ridges which run from the snout to the eyes and the bone behind the eye has a spine, with another spine at the symphysis of the jaws. The wide mouth is armed with numerous long, sharp teeth. The large gill opening is located behind the base of the pectoral fin but extends to its front too. The dorsal fin is divided into two with the first comprising 3 separate spines in the head with a few spines within a membrane above the pectoral fin while the second is supported by 8 soft rays. The first spine on the head is the angling pole, the illicium, has a flap of flesh, the esca, at its tip which is used as a lure to attract prey to within reach of the large mouth. The anal fin contains 8 soft rays and is located quite far back on the body.[10] The largest species is the club-bait goosefish (L. monodi) with a maximum published total length of 52 cm (20 in), while the smallest is L. fimbriatus with a maximum published standard length of 7.5 cm (3.0 in).[6]
Distribution
Lophiodus goosefishes are found in the tropical and subtropical parts of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.[10]
References
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lophiodes.
Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Genera in the family Lophiidae". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 3 March 2024.
Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Species in the genus Lophiodes". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 3 March 2024.
Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 508–518. doi:10.1002/9781119174844. ISBN 978-1-118-34233-6. LCCN 2015037522. OCLC 951899884. OL 25909650M.
Masaki Miya; Theodore W Pietsch; James W Orr; et al. (2010). "Evolutionary history of anglerfishes (Teleostei: Lophiiformes): a mitogenomic perspective". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 10 (58): 58. Bibcode:2010BMCEE..10...58M. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-10-58. PMC 2836326.
Christopher Scharpf (14 November 2022). "Order LOPHIIFORMES (part 1): Families LOPHIIDAE, ANTENNARIIDAE, TETRABRACHIIDAE, LOPHICHTHYIDAE, BRACHIONICHTHYIDAE, CHAUNACIDAE and OGCOCEPHALIDAE". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf. Retrieved 3 March 2024.
Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2024). Species of Lophiodes in FishBase. February 2024 version.
Ho, H.-C. & Shao, K.-T. (2008). "A new species of anglerfish (Lophiidae: Lophiodes) from the western Pacific" (PDF). Ichthyological Research. 55 (4): 367–373. doi:10.1007/s10228-008-0057-y. S2CID 13100568.
Ho, H.-C.; Séret, B.; Shao, K.-T. (2011). "Records of anglerfishes (Lophiiformes: Lophiidae) from the western South Pacific Ocean, with descriptions of two new species". Journal of Fish Biology. 79 (7): 1722–1745. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2011.03106.x. PMID 22141884.
Ho, H.-C.; Bineesh, K. K.; Akhilesh, K. V. (2014). "Rediscovery of Lophiodes triradiatus (Lloyd, 1909), a senior synonym of L. infrabrunneus Smith and Radcliffe (Lophiiformes: Lophiidae)". Zootaxa. 3786 (5): 587–592. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3786.5.6. PMID 24869556.
"Genus: Lophiodes, Anglerfishes, Goosefish, Goosefishes". Shorefishes of the Greater Caribbean online information system. Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute. Retrieved 3 March 2024.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

