Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Euteleosteomorpha
Subcohors: Neoteleostei
Infracohors: Eurypterygia
Sectio: Ctenosquamata
Subsectio: Acanthomorphata
Divisio/Superordo: Acanthopterygii
Ordo: Scorpaeniformes
Subordo: Scorpaenoidei
Familia: Triglidae
Genus: Lepidotrigla
Name
Lepidotrigla Günther, 1860
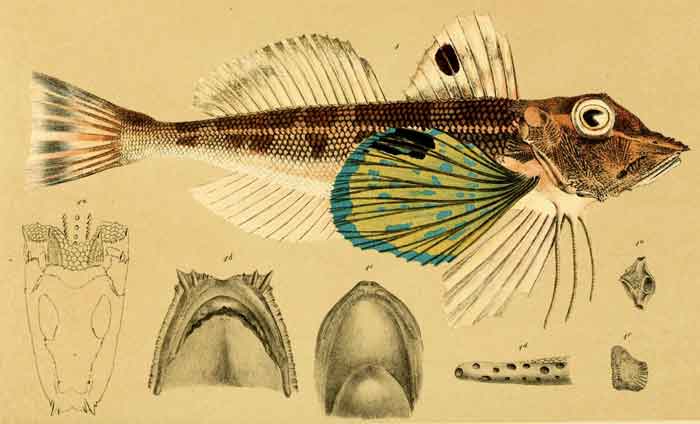
Lepidotrigla vanessa
Lepidotrigla is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. These gurnards are found in the Eastern Atlantic, Indian and Western Pacific Oceans.
Taxonomy
Lepidotrigla was first described as a genus in 1860 by the German-born British herpetologist and ichthyologist Albert Günther with Trigla aspera, which had been described in 1829 from the Mediterranean Sea by Georges Cuvier,[2] as the type species. The genus is classified within the subfamily Triglinae, the nominate subfamily of the family Triglidae.[1] The genus name prefixes Trigla, the type genus of the Triglidae. with lepido, "scaled", a reference to the larger scales on these gurnards in comparison to those on Trigla.[3]
Species
Lepidotrigla is the most speciose genus in the Triglidae[4] and has 58 species classified within it:[5][2]
Lepidotrigla abyssalis D. S. Jordan & Starks, 1904
Lepidotrigla alata (Houttuyn, 1782)
Lepidotrigla alcocki Regan, 1908
Lepidotrigla annamarae del Cerro & Lloris, 1997
Lepidotrigla argus J. D. Ogilby, 1910 (Long-finned gurnard)
Lepidotrigla argyrosoma Fowler, 1938
Lepidotrigla bentuviai Richards & Saksena, 1977 (Twohorn gurnard)
Lepidotrigla bispinosa Steindachner, 1898 (Bullhorn gurnard)
Lepidotrigla brachyoptera F. W. Hutton, 1872 (Scaly gurnard)
Lepidotrigla cadmani Regan, 1915 (Scalebreast gurnard)
Lepidotrigla calodactyla J. D. Ogilby, 1910 (Drab longfin gurnard)
Lepidotrigla carolae Richards, 1968 (Carol's gurnard)
Lepidotrigla cavillone (Lacépède, 1801) (Large-scaled gurnard)
Lepidotrigla deasoni Herre & Kauffman, 1952
Lepidotrigla dieuzeidei Blanc & Hureau, 1973 (Spiny gurnard)
Lepidotrigla eydouxii Sauvage, 1878
Lepidotrigla faurei Gilchrist & W. W. Thompson, 1914 (Scalybreast gurnard)
Lepidotrigla firmisquamis Prokofiev & Yato, 2020
Lepidotrigla grandis J. D. Ogilby, 1910 (Supreme gurnard)
Lepidotrigla guentheri Hilgendorf, 1879
Lepidotrigla hime Matsubara & Hiyama, 1932
Lepidotrigla japonica (Bleeker, 1854)
Lepidotrigla jimjoebob Richards, 1992
Lepidotrigla kanagashira Kamohara, 1936
Lepidotrigla kishinouyi Snyder, 1911
Lepidotrigla larsoni del Cerro & Lloris, 1997 (Swordtip gurnard)
Lepidotrigla lepidojugulata S. Z. Li, 1981
Lepidotrigla longifaciata Yato, 1981
Lepidotrigla longimana S. Z. Li, 1981
Lepidotrigla longipinnis Alcock, 1890
Lepidotrigla macracaina Gomon & Kawai 2018
Lepidotrigla macrobrachia Fowler, 1938
Lepidotrigla maculapinna Gomon & Kawai 2018
Lepidotrigla marisinensis (Fowler, 1938)
Lepidotrigla microptera Günther, 1873
Lepidotrigla modesta Waite, 1899 (Grooved gurnard)
Lepidotrigla mulhalli W. J. Macleay, 1884 (Rough-snouted gurnard)
Lepidotrigla multispinosa J. L. B. Smith, 1934 (Indian Ocean spiny gurnard)
Lepidotrigla musorstom del Cerro & Lloris, 1997
Lepidotrigla nana del Cerro & Lloris, 1997
Lepidotrigla oglina Fowler, 1938
Lepidotrigla omanensis Regan, 1905 (Oman gurnard)
Lepidotrigla papilio (Cuvier, 1829) (Australian spiny gurnard)
Lepidotrigla pectoralis Fowler, 1938
Lepidotrigla pleuracanthica J. Richardson, 1845 (Eastern spiny gurnard)
Lepidotrigla psolokerkos Gomon & Psomadakis, 2018
Lepidotrigla punctipectoralis Fowler, 1938 (Finspot gurnard)
Lepidotrigla robinsi Richards, 1997
Lepidotrigla russelli del Cerro & Lloris, 1995 (Smooth gurnard)
Lepidotrigla sayademalha Richards, 1992
Lepidotrigla sereti del Cerro & Lloris, 1997
Lepidotrigla spiloptera Günther, 1880 (Spotwing gurnard)
Lepidotrigla spinosa Gomon, 1987 (Shortfin gurnard)
Lepidotrigla tanydactyla Gomon & Kawai 2018
Lepidotrigla umbrosa J. D. Ogilby, 1910 (Blackspot gurnard)
Lepidotrigla vanessa (J. Richardson, 1839) (Butterfly gurnard)
Lepidotrigla vaubani del Cerro & Lloris, 1997
Lepidotrigla venusta Fowler, 1938
Characteristics
Lepidotrigla gurnards are characterised by having the 3 lower rays of the pectoral fin free of the fin membrane and a scaled tail, like the other Triglid gurnards. The bucklers, bony plate at the base of the dorsal fin spines and rays, have with sharp spines on their rears along the whole length of both first and seconddorsal fins.[6] The groobe behind the eyes of these fishes may be complete, running from one side of the head to the other, or there may be just a furrow behind each eye. There are large, ctenoid scales on the body, although some species have cycloid scales on the belly. There are fewer tha than 70 scales in the lateral line. There may, or may not be vomerine teeth.[7] These relatively small grnards vary in size from the smallest, the spotwing gurnard (L. spiloptera) with a maximum published total length of 10 cm (3.9 in), to the scalebreast gurnard (L. cadmani) and L. microptera, both having maximum published total length of 30 cm (12 in).[5]
Distribution
Lepidotrigla gurnards are found in the tropical and warm temperate waters of the eastern Atlantic, Indian and Western Pacific Oceans, with one species L. jimjoebob being found as far east as the Line Islands in the eastern central Pacific.[5]
See also
List of prehistoric bony fish
References
Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Genera in the family Triglinae". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 19 June 2022.
Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Species in the genus Lepidotrigla". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 19 June 2022.
Christopher Scharpf & Kenneth J. Lazara, eds. (19 June 2021). "Order Perciformes (Part 12): Suborder Triglioidei: Families Triglidae and Peristediidae". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf and Kenneth J. Lazara. Retrieved 17 June 2022.
Gomon, M. F. and T. Kawai (2018). "A review of Indonesia's Indian Ocean species of Lepidotrigla gurnards (Teleostei: Scorpaeniformes: Triglidae) with descriptions of three new species from southern coastal waters" (PDF). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 66: 624–651.
Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2022). Species of Lepidotrigla in FishBase. February 2022 version.
Richards W.J. (1999). "Triglidae Gurnards, sea robins (also, armoured gurnards, armoured sea robins)". In K.E. Carpenter and V.H. Niem (eds.). FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific. Vol. 4. Bony fishes part 2 (Mugilidae to Carangidae). Rome, FAO. pp. 2359–2363. ISBN 92-5-104301-9.
Del Cerro L & D. Lloris (1997). Séret, B. (ed.). "Gurnard Fishes (Scorpaeniformes, Triglidae) from off New Caledonia, with description of five new species". Mémoires du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris (N. S.) (Série A) Zoologie. Résultats des Campagnes MUSORSTOM, v. 17. 174: 91–124.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

