Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Euteleosteomorpha
Subcohors: Neoteleostei
Infracohors: Eurypterygia
Sectio: Ctenosquamata
Subsectio: Acanthomorphata
Divisio/Superordo: Paracanthopterygii
Series: Zeiogadaria
Subseries: Gadariae
Ordo: Gadiformes
Familia: Gadidae
Subfamilia: Gadinae
Genus: Eleginus
Species: Eleginus nawaga
Name
Eleginus nawaga (Kölreuter, 1770)
Synonyms
Gadus nawaga Kölreuter, 1770
Eleginus navaga Essipov, 1941
References
Koelreuter, I. T. 1770. Descriptio piscis, e gadorum genere, russis nawaga dicti, historico-anatomica. Novi Commentarii Academiae Scientiarum Imperialis Petropolitanae v. 14 (1769): 484–497, Pl. 12.
Eleginus nawaga – Taxon details on Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS).
Daniel M. Cohen, Tadashi Inada, Tomio Iwamoto, Nadia Scialabba: FAO species catalogue. Vol. 10. Gadiform fishes of the world (Order Gadiformes). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of cods, hakes, grenadiers and other gadiform fishes known to date. FAO Fisheries Synopsis. No. 125, Vol. 10. Rome, FAO. 1990. S. 60–61. (PDF)
Vernacular names
català: Navaga
Deutsch: Europäische Navaga
polski: nawaga europejska
русский: Северная навага
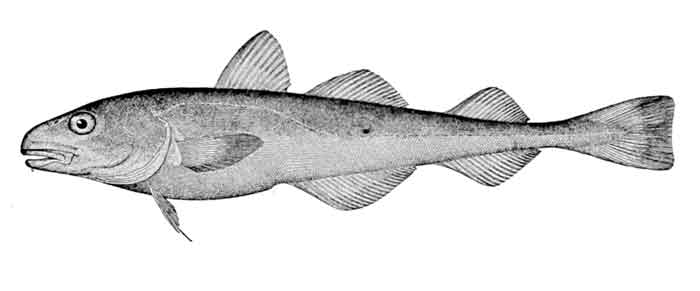
The navaga (Eleginus nawaga) is a relatively small species of fish in the cod family Gadidae. It inhabits the European arctic and subarctic waters of the Barents, White, and Kara seas, from the Kola Bay to the Ob River estuary.[1][2]
Navaga fish usually occur at shallow depths, along shores with soft bottoms, close to the ice and on the continental shelf. In winter, they live in nearshore waters, where spawning takes place. They are often found in estuaries and can enter fresh water in rivers. In summer, they return to open waters. They feed on crustaceans, benthic animals, and small fish. They can grow to at least to 42 cm but typical adult size is smaller, being only 15–25 cm in the White Sea.[1]
The navaga is commercially fished mainly in the winter in the bays of the White Sea.[1] The European navaga is a close relative of the saffron cod (E. gracilis), a Pacific sister species.
References
Daniel M. Cohen; Tadashi Inada; Tomio Iwamoto & Nadia Scialabba, eds. (1990). FAO species catalogue. Vol. 10. Gadiform fishes of the world (Order Gadiformes). An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Cods, Hakes, Grenadiers and other Gadiform Fishes Known to Date. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. pp. 36–37. ISBN 978-92-5-102890-2.
Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2022). "Eleginus nawaga" in FishBase. February 2022 version.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

