Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Euteleosteomorpha
Subcohors/Superordo: Protacanthopterygii
Ordo: Salmoniformes
Familia: Salmonidae
Subfamilia: Coregoninae
Genus: Coregonus
Species: Coregonus albula
Subspecies: C. a. albula – C. a. vodlosericus
Name
Coregonus albula (Linnaeus, 1758)
Original combination: Salmo albula
Synonyms
Salmo vimba Linnaeus, 1758
Coregonus albula subsp. olonensis P.G.Borisov, 1924
Coregonus albula natio pereslawicus P.G.Borisov, 1924
References
Linnaeus, C. 1758. Systema Naturae per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis, Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata. Holmiæ: impensis direct. Laurentii Salvii. i–ii, 1–824 pp DOI: 10.5962/bhl.title.542: 310. Open access Reference page.
Coregonus albula – Taxon details on Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS).
Coregonus albula in FishBase,
Froese, R. & Pauly, D. (eds.) 2024. FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication, www.fishbase.org, version 02/2024.
IUCN: Coregonus albula (Least Concern)
Vernacular names
беларуская (тарашкевіца): Сялява
беларуская: Сялява
català: Corègon blanc
kaszëbsczi: Mòrénka
čeština: Síh malý
Deutsch: Kleine Maräne
English: vendace, European cisco
español: Corégono blanco
eesti: Rääbis, Rääbus, Rääbusk, Salakas
suomi: muikku
français: Corégone blanc
magyar: Törpemaréna
italiano: Coregone bianco
日本語: モトコクチマス
lietuvių: Seliava
Nederlands: Kleine marene
norsk nynorsk: Lagasild
norsk: Lagesild
polski: Sielawa
русский: Европейская ряпушка
svenska: siklöja
Tiếng Việt: Cá hồi trắng châu Âu
Coregonus albula, known as the vendace or as the European cisco,[1] is a species of freshwater whitefish in the family Salmonidae. It is found in lakes in northern Europe, especially Finland, Latvia,[2] Lithuania, Sweden, Russia and Estonia, and in some lakes of Norway, the United Kingdom, northern Germany, and Poland. It is also found in diluted brackish water in the Gulfs of Finland and Bothnia, both of which are in the Baltic Sea.[3]
The length of an adult is normally about 20 cm (8 in). The maximum age is about ten years.[3]
Fried vendace is a popular summertime food in Finland.
The vendace is traditionally the most important target of freshwater fisheries in parts of Fennoscandia and Russia. Vendace roe is considered a delicacy, which has been granted a PDO status in the Swedish Bothnian Bay archipelago (Kalix löjrom).
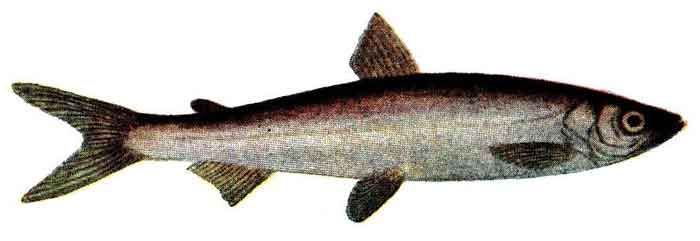
Description
The vendace is a slim and streamlined fish with an adipose fin - an additional small fin on the back between the dorsal fin and the tail (caudal fin) which is typical in the salmon family. Its lower jaw is longer than the upper one. It is similar in appearance to both the common whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus sensu lato), whose upper jaw is longer than its lower one, and the peled (Coregonus peled), whose jaws are of equal length. The back is bluish green or brown, the flanks are silvery and the belly white. This fish seldom grows more than 30 cm (12 in) long.[4]
Biology
Vendace mainly feed on zooplankton, such as small crustaceans and their larvae, but larger fish also feed on floating insects and fish fry. The fish live in schools made up of large groups of individuals. They lay their eggs on pebbly or sandy ground, some in shallow water and others at depths of down to 20 m (66 ft). The fish mature at a young age and most spawn for the first time in their second year, but a few may breed in their first autumn.[4]
Systematics
Finns fishing vendace with seine on Puruvesi lake in Finland on February 1964.
The European vendace is very closely related to the Siberian Coregonus sardinella (sardine cisco) and also to C. peled, although phenotypic differences are clear.[5]
Within the vendace, taxonomic subdivisions have been suggested both on geographical grounds and between sympatric ecotypes. FishBase lists the British populations of vendace as a separate species, Coregonus vandesius,[6] but this distinction is not accepted by all scientists.[7]
Coregonus albula generally breeds in the autumn, but in several North European lakes distinct spring-spawning populations of vendace exist, some of which have been described as separate species: in Sweden, as Coregonus trybomi, and in two lakes of northern Germany, as Coregonus fontanae and Coregonus lucinensis. These populations are sympatric with autumn-spawning vendace and seem to have evolved post-glacially from them independently in each lake.[8][9]
Seven vendaces in the coat of arms of Viitasaari
See also
Cisco
Nanbanzuke
References
Freyhof, J. (2016) [errata version of 2011 assessment]. "Coregonus albula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2011: e.T5360A97801719. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T5360A11122508.en. Retrieved 19 December 2023.
"repsis - Coregonus albula (L.) - Zivis - Latvijas daba".
Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2015). "Coregonus albula" in FishBase. November 2015 version.
"Vendace: Coregonus albula (L.)". NatureGate. Retrieved 2013-12-18.
Bernatchez L, Colombani F, Dodson JJ (1991) Phylogenetic relationships among the subfamily Coregoninae as revealed by mitochondrial DNA restriction analysis Journal of Fish Biology 39 (Suppl A):283-290.
Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2010). "Coregonus vandesius" in FishBase. January 2010 version.
Winfield, Ian J.; Fletcher, Janis M.; James, J. Ben (2004). "Conservation ecology of the vendace in Bassenthwaite Lake and Derwent Water, U.K." (PDF). Annales Zoologici Fennici. 41: 155–164.
Schulz, M.; Freyhof, J. (October 2002). "Coregonus fontanae, a new spring-spawning cisco from Lake Stechlin, northern Germany (Salmoniformes: Coregonidae)" (PDF). Ichthyological Exploration of Freshwaters. 14 (3): 209–216. ISSN 0936-9902. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2004-01-21.
Schulz, M.; Freyhof, J.; Saint‐Laurent, R.; Østbye, K.; Mehner, T. & Bernatchez, L. (March 13, 2006). "Evidence for independent origin of two spring‐spawning ciscoes (Salmoniformes: Coregonidae) in Germany". Journal of Fish Biology. 68 (A): 119–135. doi:10.1111/j.0022-1112.2006.01039.x. ISSN 0022-1112. Archived from the original on January 5, 2013.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

