Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Euteleosteomorpha
Subcohors: Neoteleostei
Infracohors: Eurypterygia
Sectio: Ctenosquamata
Subsectio: Acanthomorphata
Divisio/Superordo: Acanthopterygii
Subdivisio: Percomorphaceae
Series: Eupercaria
Ordo: Centrarchiformes
Subordo: Cirrhitoidei
Superfamilia: Cirrhitoidea
Familia: Chironemidae
Genus: Chironemus
Species: C. bicornis – C. delfini – C. georgianus – C. marmoratus – C. microlepis
Name
Chironemus Cuvier, 1829
References
Chironemus – Taxon details on Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS).
Chironemus species list in FishBase,
Froese, R. & Pauly, D. (eds.) 2024. FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication, www.fishbase.org, version 02/2024.
Vernacular names
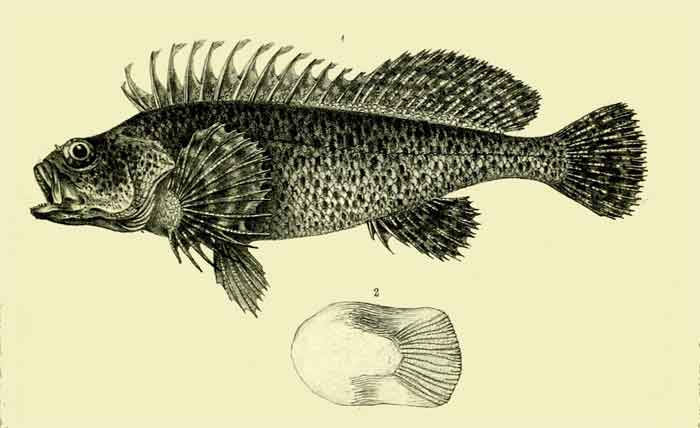
Chironemus maculosus
Chironemus is a genus of marine ray finned fish, commonly known as kelpfishes, belonging to the family Chironemidae. They are found in the temperate waters of the Southern Pacific Ocean.
Taxonomy
The Kelpfishes were placed in the monogeneric family Chironemidae in 1862 by the American ichthyologist Theodore Nicholas Gill.[1] The genus had been described in 1829 by the French zoologist Georges Cuvier when he had described the type species Chironemus georgianus.[2] The family is regarded as part of the superfamily Cirrhitoidea, which is placed within the order Perciformes in the 5th Edition of Fishes of the World,[3] however other authorities place this clade within a new order within the wider Percomorpha, Centrarchiformes.[4] The name of the genus is from Greek cheir meaning "hands" and nema meaning "thread".[5]
Species
The currently recognized species in this genus are:[6]
Chironemus bicornis (Steindachner, 1898)
Chironemus delfini (Porter, 1914)
Chironemus georgianus G. Cuvier, 1829 (tasselled kelpfish)
Chironemus maculosus (J. Richardson, 1850) (silver spot)
Chironemus marmoratus Günther, 1860 (large kelpfish)
Chironemus microlepis Waite, 1916 (smallscale kelpfish)
Characteristics
The fishes within the genus Chironemus have tubular nostrils which have tufts of cirri. They have moderately sized cycloid scales. The continuous dorsal fin has a long base and robust spines. The spiny part of the dorsal fin is separated from the soft rayed part by distinct incision. The anal fin has small with thick spines. The large pectoral fins have their upper fin rays branched and 6 the six lower rays are notably more robust and are unbranched.[7] These high backed fishes resemble the morwongs belonging to the family Cheilodactylidae but they have a truncate caudal fin and fewer soft rays in the anal fin. They typically have a marbled colour pattern camouflaging them in their preferred rocky habitat.[8] The dorsal dins of these fishes contain 14-16 spines and 15-21 soft rays while their anal fins contain 6-8 soft rays. They have vomerine teeth but there are no teeth on the palatine. They grow to a maximum of approximately 40 cm (16 in).[4]
Distribution and habitat
Chironemus kelpfishes are found in the southern Pacific Ocean off Australia, New Zealand and the western coast of South America off Peru and Chile.[3] They are coastal fishes adapted to living in shallow waters where they are exposed to waves.[7]
Biology
Chironemus kelpfishes feed on benthic invertebrates. They lodge themselves into small niches or interstices in rocks holding their bodies in place with their large pectoral fins.[7]
Wikispecies has information related to Chironemus.
References
Richard van der Laan; William N. Eschmeyer & Ronald Fricke (2014). "Family-group names of Recent fishes". Zootaxa. 3882 (2): 001–230. Retrieved 24 July 2021.
Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Genera in the family Chironemidae". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 24 July 2021.
J. S. Nelson; T. C. Grande; M. V. H. Wilson (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). Wiley. p. 459. ISBN 978-1-118-34233-6. Archived from the original on 2019-04-08. Retrieved 2021-07-24.
Froese, Rainer, and Daniel Pauly, eds. (2021). "Chironemidae" in FishBase. June 2021 version.
Christopher Scharpf & Kenneth J. Lazara, eds. (25 February 2021). "Order CENTRARCHIFORMES: Families CENTRARCHIDAE, ELASSOMATIDAE, ENOPLOSIDAE, SINIPERCIDAE, APLODACTYLIDAE, CHEILODACTYLIDAE, CHIRONEMIDAE, CIRRHITIDAE, LATRIDAE, PERCICHTHYIDAE, DICHISTIIDAE, GIRELLIDAE, KUHLIIDAE, KYPHOSIDAE, OPLEGNATHIDAE, TERAPONTIDAE, MICROCANTHIDAE and SCORPIDIDAE". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf and Kenneth J. Lazara. Retrieved 24 July 2021.
Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2021). Species of Chironemus in FishBase. June 2021 version.
Martin F. Gomon & Dianne J. Bray. "Kelpfishes, CHIRONEMIDAE". Fishes of Australia. Museums Victoria. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
"Chironemidae". Encyclopedia.com. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 24 July 2021.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

