Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Cladus: Sarcopterygii
Cladus: Rhipidistia
Cladus: Tetrapodomorpha
Cladus: Eotetrapodiformes
Cladus: Elpistostegalia
Superclassis: Tetrapoda
Cladus: Reptiliomorpha
Cladus: Amniota
Classis: Reptilia
Cladus: Eureptilia
Cladus: Romeriida
Subclassis: Diapsida
Cladus: Sauria
Infraclassis: Archosauromorpha
Cladus: Crurotarsi
Divisio: Archosauria
Cladus: Avemetatarsalia
Cladus: Ornithodira
Subtaxon: Dinosauromorpha
Cladus: Dinosauriformes
Cladus: Dracohors
Cladus: Dinosauria
Cladus: Saurischia
Cladus: Eusaurischia
Subordo: Theropoda
Cladus: Neotheropoda
Cladus: Averostra
Cladus: Tetanurae
Cladus: Avetheropoda
Cladus: Coelurosauria
Cladus: Tyrannoraptora
Cladus: Maniraptoromorpha
Cladus: Maniraptoriformes
Cladus: Maniraptora
Cladus: Pennaraptora
Cladus: Paraves
Cladus: Eumaniraptora
Cladus: Avialae
Infraclassis: Aves
Cladus: Avebrevicauda
Cladus: Pygostylia
Cladus: Ornithothoraces
Cladus: Ornithuromorpha
Cladus: Carinatae
Parvclassis: Neornithes
Cohors: Neognathae
Cladus: Neoaves
Ordo: Piciformes
Familia: Picidae
Subfamilia: Picinae
Genus: Picus
Species: P. awokera – P. canus – P. chlorolophus – P. dedemi – P. erythropygius – P. puniceus – P. rabieri – P. sharpei – P. squamatus – P. vaillantii – P. viridanus – P. viridis – P. vittatus – P. xanthopygaeus
Nomina dubia: P. hirundinaceus – P. semirostris
Name
Picus Linnaeus, 1758
Gender: masculine
Typus: Picus viridis Linnaeus, 1758
Synonymy
Venilia Bonaparte, 1850 Consp.Gen.Avium p. 128 BHL
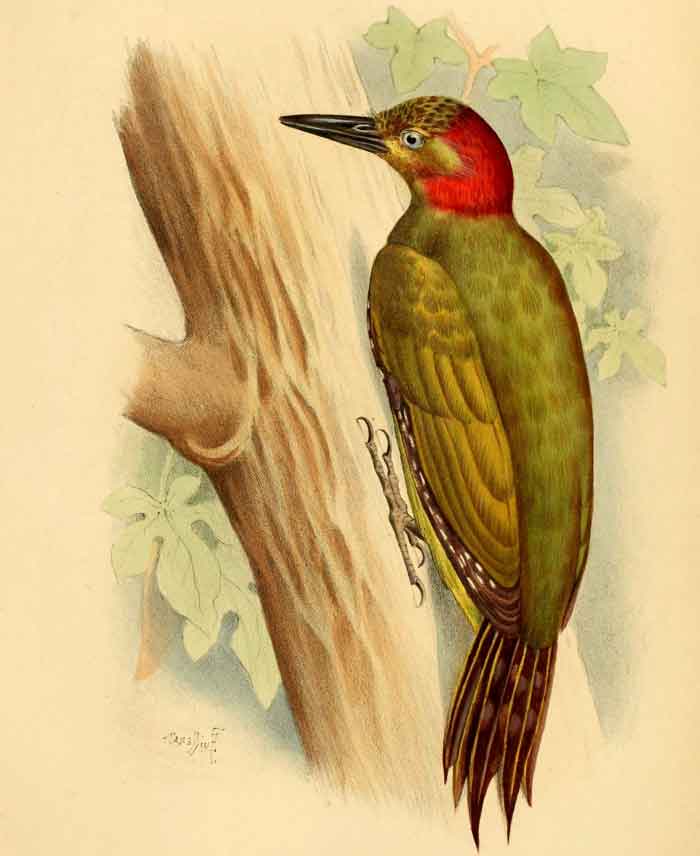
Picus rabieri
References
Linnaeus, C. 1758. Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Editio Decima, Reformata. Tomus I. Holmiæ (Stockholm): impensis direct. Laurentii Salvii. 824 pp. DOI: 10.5962/bhl.title.542 BHL p. 112 BHL Reference page.
Picus is a genus of birds in the woodpecker family. It has representatives in Europe, Asia and North Africa. The genus name is Latin for "woodpecker". The genus Picus was erected by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae.
These are large woodpeckers, typically with green upperparts. They are found in forests or more open woodland, and lay their white eggs in a tree hole nest, typically on a bed of wood chips. Picus woodpeckers are primarily insect eaters, with several species specialising in taking ants or termites. Some species will also consume fruit or eggs. Insects are captured by a rapid outward flick of the long tongue and gummed to its tip by sticky saliva. This genus is less completely arboreal than some other woodpecker groups, and its members often feed on the ground, attacking anthills or termitaries.
Taxonomy
The genus Picus was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae.[2] The genus name is the Latin word for a woodpecker. Picus was a figure in Roman mythology, the first king of Latium who was changed into a woodpecker by the sorceress Circe.[3] Of the 13 species in the genus listed by Linnaeus, the English naturalist William John Swainson designated the European green woodpecker (Picus viridis) as the type species.[4]
The genus contains 14 species:[5]
Image Common Name Scientific name Distribution
Lesser yellownape Picus chlorolophus India, Bhutan, Nepal, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka eastwards to Thailand, Burma, Cambodia, Laos, Indonesia, Malaysia and Vietnam.
Crimson-winged woodpecker Picus puniceus Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, and Thailand.
Streak-breasted woodpecker Picus viridanus southeastern Bangladesh to central Malay Peninsula.
Laced woodpecker Picus vittatus Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam.
Streak-throated woodpecker Picus xanthopygaeus Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia
Scaly-bellied woodpecker Picus squamatus Afghanistan, Iran, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Turkmenistan.
Japanese green woodpecker Picus awokera Japan.
European green woodpecker Picus viridis Europe south from southern Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Asia Minor, northern Iran and south-west Turkmenistan.
Iberian green woodpecker Picus sharpei Europe
Levaillant's woodpecker Picus vaillantii Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia in northwest Africa
Red-collared woodpecker Picus rabieri Cambodia, China, Laos, and Vietnam.
Black-headed woodpecker Picus erythropygius Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Grey-headed woodpecker Picus canus Central, Northern and Eastern Europe, as well as a wide belt south of the boreal coniferous forests across Asia all the way to the Pacific coast, Sakhalin and Hokkaidō
Sumatran woodpecker Picus dedemi Indonesia
Former species
The following were formerly included in Picus, but are now placed in Chrysophlegma.
Greater yellownape, Chrysophlegma flavinucha
Checker-throated woodpecker, Chrysophlegma mentalis
Banded woodpecker, Chrysophlegma miniaceus
An extinct woodpecker has been described from a fossil of a left tarsometatarsus dating from late Miocene. It may belong to this genus and has been given the binomial name Picus peregrinabundus.[6]
References
For instance: John Gould – The Birds of Great Britain (vol. 3 (1873), Plate 74) for the European green woodpecker: Gecinus viridis. See also: Iberian green woodpecker, originally named Gecinus sharpei.
Linnaeus, Carl (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1 (10th ed.). Holmiae (Stockholm): Laurentii Salvii. p. 112.
Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 306. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
Swainson, William John (1820). Zoological illustrations, or, Original figures and descriptions of new, rare, or interesting animals. Vol. 1. London: Baldwin, Cradock, and Joy; and W. Wood. Plate 4 text.
Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (August 2022). "Woodpeckers". IOC World Bird List Version 12.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
Kessler, Jenő (Eugen) (2016). "Picidae in the European fossil, subfossil and recent bird faunas and their osteological characteristics". Ornis Hungarica. 24 (1): 96–114. doi:10.1515/orhu-2016-0006.Picus is a genus of birds in the woodpecker family. It has representatives in Europe, Asia and North Africa. The genus name is Latin for "woodpecker". The genus Picus was erected by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae.
These are large woodpeckers, typically with green upperparts. They are found in forests or more open woodland, and lay their white eggs in a tree hole nest, typically on a bed of wood chips. Picus woodpeckers are primarily insect eaters, with several species specialising in taking ants or termites. Some species will also consume fruit or eggs. Insects are captured by a rapid outward flick of the long tongue and gummed to its tip by sticky saliva. This genus is less completely arboreal than some other woodpecker groups, and its members often feed on the ground, attacking anthills or termitaries.
Taxonomy
The genus Picus was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his Systema Naturae.[2] The genus name is the Latin word for a woodpecker. Picus was a figure in Roman mythology, the first king of Latium who was changed into a woodpecker by the sorceress Circe.[3] Of the 13 species in the genus listed by Linnaeus, the English naturalist William John Swainson designated the European green woodpecker (Picus viridis) as the type species.[4]
The genus contains 14 species:[5]
| Image | Common Name | Scientific name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Lesser yellownape | Picus chlorolophus | India, Bhutan, Nepal, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka eastwards to Thailand, Burma, Cambodia, Laos, Indonesia, Malaysia and Vietnam. |
 |
Crimson-winged woodpecker | Picus puniceus | Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, and Thailand. |
 |
Streak-breasted woodpecker | Picus viridanus | southeastern Bangladesh to central Malay Peninsula. |
 |
Laced woodpecker | Picus vittatus | Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam. |
 |
Streak-throated woodpecker | Picus xanthopygaeus | Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia |
 |
Scaly-bellied woodpecker | Picus squamatus | Afghanistan, Iran, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Turkmenistan. |
 |
Japanese green woodpecker | Picus awokera | Japan. |
 |
European green woodpecker | Picus viridis | Europe south from southern Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Asia Minor, northern Iran and south-west Turkmenistan. |
 |
Iberian green woodpecker | Picus sharpei | Europe |
 |
Levaillant's woodpecker | Picus vaillantii | Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia in northwest Africa |
 |
Red-collared woodpecker | Picus rabieri | Cambodia, China, Laos, and Vietnam. |
 |
Black-headed woodpecker | Picus erythropygius | Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam. |
 |
Grey-headed woodpecker | Picus canus | Central, Northern and Eastern Europe, as well as a wide belt south of the boreal coniferous forests across Asia all the way to the Pacific coast, Sakhalin and Hokkaidō |
| Sumatran woodpecker | Picus dedemi | Indonesia |
Former species
The following were formerly included in Picus, but are now placed in Chrysophlegma.
Greater yellownape, Chrysophlegma flavinucha
Checker-throated woodpecker, Chrysophlegma mentalis
Banded woodpecker, Chrysophlegma miniaceus
An extinct woodpecker has been described from a fossil of a left tarsometatarsus dating from late Miocene. It may belong to this genus and has been given the binomial name Picus peregrinabundus.[6]
References
For instance: John Gould – The Birds of Great Britain (vol. 3 (1873), Plate 74) for the European green woodpecker: Gecinus viridis. See also: Iberian green woodpecker, originally named Gecinus sharpei.
Linnaeus, Carl (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1 (10th ed.). Holmiae (Stockholm): Laurentii Salvii. p. 112.
Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 306. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
Swainson, William John (1820). Zoological illustrations, or, Original figures and descriptions of new, rare, or interesting animals. Vol. 1. London: Baldwin, Cradock, and Joy; and W. Wood. Plate 4 text.
Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (August 2022). "Woodpeckers". IOC World Bird List Version 12.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
Kessler, Jenő (Eugen) (2016). "Picidae in the European fossil, subfossil and recent bird faunas and their osteological characteristics". Ornis Hungarica. 24 (1): 96–114. doi:10.1515/orhu-2016-0006.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

