Classification System: APG IV
Superregnum: Eukaryota
Regnum: Plantae
Cladus: Angiosperms
Cladus: Monocots
Ordo: Alismatales
Familia: Cymodoceaceae
Genus: Thalassodendron
Species: Thalassodendron ciliatum
Name
Thalassodendron ciliatum (Forssk.) Hartog, Verh. Kon. Ned. Akad. Wetensch., Afd. Natuurk., Sect. 2, 59(1): 188 (1970)
Synonyms
Basionym
Zostera ciliata Forssk., Fl. Aegypt.-Arab.: 157 (1775).
Homotypic
Thalassia ciliata (Forssk.) K.D.Koenig, Ann. Bot. (König & Sims) 2: 97 (1805).
Cymodocea ciliata (Forssk.) Ehrenb. ex Asch., Sitzungsber. Ges. Naturf. Freunde Berlin 1867: 3 (1867).
Phucagrostis ciliata (Forssk.) Ehrenb. & Hemprich, Symb. Phys., Bot.: t. 6 (1900).
Distribution
Native distribution areas:
Continental: Red Sea to W. Indian Ocean and Caroline Is. (Palau)
Aldabra; Andaman Is.; Caroline Is.; Chagos Archipelago; Cocos (Keeling) Is.; Comoros; Djibouti; Egypt; Eritrea; Iran; Jawa; Kenya; KwaZulu-Natal; Lesser Sunda Is.; Madagascar; Maldives; Maluku; Mauritius; Mozambique; Mozambique Channel I; New Guinea; Palestine; Philippines; Queensland; Saudi Arabia; Seychelles; Sinai; Socotra; Solomon Is.; Somalia; Sudan; Sulawesi; Tanzania; Yemen
References: Brummitt, R.K. 2001. TDWG – World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions, 2nd Edition
References
Primary references
Hartog, C. den 1970. Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Nederlandsche Akademie van Wetenschappen. Afdeeling Natuurkunde; Tweede Sectie 59(1): 188.
Links
Govaerts, R. et al. 2014. Thalassodendron ciliatum in Kew Science Plants of the World Online. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published online. Accessed: 2014 Nov. 22. Reference page.
International Plant Names Index. 2014. Thalassodendron ciliatum. Published online. Accessed: Nov. 22 2014.
Tropicos.org 2014. Thalassodendron ciliatum. Missouri Botanical Garden. Published online. Accessed: 22 Nov. 2014.
Vernacular names
中文: 全楔草
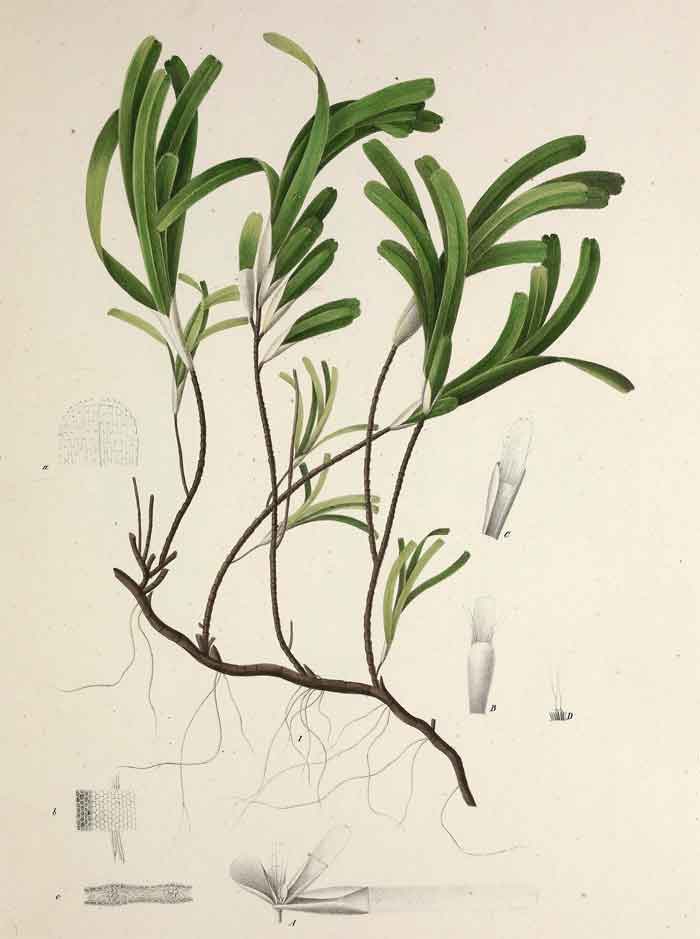
Thalassodendron ciliatum, the sickle-leaved cymodocea,[3] is a species of plant in the Thalassodendron genus of seagrasses in the family Cymodoceaceae.
Distribution
Thalassodendron ciliatum has a wide distribution throughout the Indo-Pacific region, but has variable abundances throughout its range. This seagrass has been recorded from the western Philippines to Borneo and Singapore, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, the Caroline Islands, Vanuatu, Australia, India and the Maldives. It is also common from the Gulf of Oman to the Red Sea down to South Africa, Madagascar, the Seychelles, the Comores, the Mascarenes and parts of Malesia and the Solomon Islands.[4][5][6][7]
Thalassodendron ciliatum facts
Thalassodendron ciliatum has a wide distribution throughout the Indo-Pacific region, but has variable abundances throughout its range.
Thalassodendron ciliatum is typically found in the upper part of the sublittoral zone to depths down to 17 meters.
Dense monospecific meadows form in deeper localities on sandy bottoms, coral reefs and sand-covered rocks.
Thalassodendron ciliatum is a fast-growing seagrass; however, it is slow to re-colonize.
This species is susceptible to intense grazing by sea urchins. Anthropogenic stressors on this species include coastal development, pollution, eutrophication, seaweed farming, beach seines and drag net trawling.[4]
Leaf morphology
Red or red striped leaves, Linear and falcate.10–15 cm long and 6-13mm wide with an average width of 10mm, Leaf margins are almost entire with serrations visible towards the tip, Leaf sheath is wide and compressed and measuring 15-30mm long and appears pink in color.[4]
Rhizome, stem and roots
Thick, well-developed rhizome up to 0.5 cm thick with the mat formed by the rhizome approximately 5–10 cm thick. One to two stems are present at every fourth internode along the rhizome, the first stem is either unbranched or slightly branched and 10–65 cm long while The second stem is usually under-developed, if present, and in the form of a bud. Roots occur in groups of 1-5 and range from slightly to highly branched and occur on the internode before the stem.[4]
References
Short, F.T., Coles, R., Waycott, M., Bujang, J.S., Fortes, M., Prathep, A., Kamal, A.H.M., Jagtap, T.G., Bandeira, S., Freeman, A., Erftemeijer, P., La Nafie, Y.A., Vergara, S., Calumpong, H.P. & Makm, I. (2010). "Thalassodendron ciliatum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010: e.T173375A7002484. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T173375A7002484.en. Retrieved 18 January 2024.
"WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Cymodocea ciliata (Forsk.) Ehr. Ex Aschers".
"Sickle-leaved Cymodocea - Thalassodendron ciliatum - Common names - Encyclopedia of Life". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 2017-02-03.
seagrassrecovery.com date of access Wednesday, December 11, 2013 Archived October 18, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
den Hartog, C. (1970) The sea-grasses of the world. Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, afd, Natuurkunde, Tweede Reeks 59: 1-275
Green E.P and Short F.T. (2003) World Atlas of Seagrasses. Prepared by the UIMEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre, University of California Press, Berkeley, USA
Short, F.T., Coles, R., Waycott, M., Bujang, J.S., Fortes, M., Prathep, A., Kamal, A.H.M., Jagtap, T.G., Bandeira, S., Freeman, A., Erftemeijer, P., La Nafie, Y.A., Vergara, S., Calumpong, H.P. & Makm, I. (2010) Thalassodendron ciliatum. In: IUCN 2012. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. . Downloaded November 2012
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

