Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Euteleosteomorpha
Subcohors: Neoteleostei
Infracohors: Eurypterygia
Sectio: Ctenosquamata
Subsectio: Acanthomorphata
Divisio/Superordo: Acanthopterygii
Ordo: Scorpaeniformes
Subordo: Scorpaenoidei
Familia: Sebastidae
Subfamilia: Sebastinae
Genus: Sebastes
Species: Sebastes aleutianus
Name
Sebastes aleutianus (Jordan & Evermann, 1898)
Type locality: Off Karluk, Kodiak Island, Shelikof Straits, Alaska, U.S.A., Albatross station 3676, about 57°30'N, 154°W, depth 110 fathoms.
Lectotype: USNM 48800
Paralectotypes: SU 12928 (3), plus specimen in ZMB 8145 (1)
Synonyms
Sebastodes aleutianus Jordan & Evermann, 1898
Sebastodes swifti Evermann & Goldsborough, 1907
Zalopyr aleutianus (Jordan & Evermann, 1898)
References
Jordan, D.S. & Evermann, B.W. 1898: The fishes of North and Middle America: a descriptive catalogue of the species of fish-like vertebrates found in the waters of North America, north of the Isthmus of Panama. Part II. Bulletin of the United States National Museum 47: i-xxx + 1241-2183. BHL
Orr, J.W. & Hawkins, S. 2008: Species of the rougheye rockfish complex: resurrection of Sebastes melanostictus (Matsubara, 1934) and a redescription of Sebastes aleutianus (Jordan and Evermann, 1898) (Teleostei: Scorpaeniformes). Fishery Bulletin 106(2): 111–134. PDF
Links
Sebastes aleutianus – Taxon details on Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). ("Synonyms" outdated)
Sebastes aleutianus in the World Register of Marine Species
Sebastes aleutianus in FishBase,
Froese, R. & Pauly, D. (eds.) 2024. FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication, www.fishbase.org, version 02/2024.
Sebastes aleutianus in Catalog of Fishes, Eschmeyer, W.N., Fricke, R. & van der Laan, R. (eds.) 2024. Catalog of Fishes electronic version.
Vernacular names
English: Rougheye rockfish
magyar: Dülledtszemű álsügér
中文: 阿留申平鲉
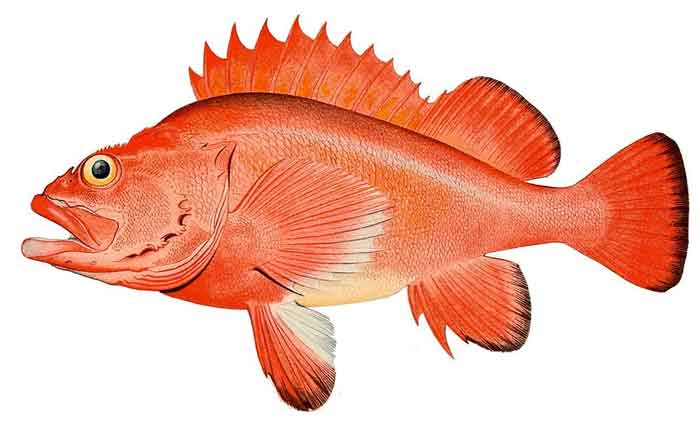
The rougheye rockfish (Sebastes aleutianus) is a rockfish of the genus Sebastes. It is also known as the blackthroat rockfish, rougheye seaperch, blacktip seaperch, longlife seaperch or the blacktip rockfish and grows to a maximum of about 97 cm (38 in) in length,[1] with the IGFA record weight being 14 lb 12 oz (6.7 kg).[2] Similar to many other members of its genus, it is extremely long-lived, and has been known to reach an age of 205 years.[3]
Taxonomy
The rougheye rockfish was first formally described as Sebastodes aleutianus in 1898 by the American ichthyologists David Starr Jordan and Barton Warren Evermann with the type locality given as off Karluk on Kodiak Island in the Shelikof Straits in Alaska.[4]
This particular taxon was previously thought to be synonymous with the blackspotted rockfish (S. melanostictus). However, the blackspotted rockfish is now recognized as a distinct and valid species. Both the blackspotted rockfish and the rougheye rockfish are currently classified within the subgenus Zalopyr.[5] The specific name means of the Aleutian Islands, Kodiak Island used to be considered to be one of the Aleutians.[6]
Description
The rougheye rockfish is so-named because of the two to ten spines found along the lower edge of its orbits. It is pink, tan or brownish with irregular patches of brown of darker color and often a darker patch at the back of the operculum. The posterior part of the lateral line is often pink. An average adult size is about 80 cm (31 in).[7]
Distribution and habitat
Rougheye rockfish are deepwater fish, and exist between 31° and 66° latitude, in the North Pacific, and specifically along the coast of Japan to the Navarin Canyon in the Bering Sea, to the Aleutian Islands, all the way south to San Diego, California.[1] It is found between 150 and 450 m, with larger fish living in deeper water than smaller ones. The temperature at these depths range from −0.3 to 5.0 °C.
These fish inhabit areas close to the seabed, often found amid boulders, rocks, and soft substrates, as well as within caves and crevices.[7]
Behavior
During certain periods, rougheye rockfish form schools, but for a considerable duration of the year, larger individuals prefer solitude or tend to move in small groups. It is considered one of the most long-lived fish species, with individuals thought to live for more than two hundred years.[7]
These fish prey on shrimps, crabs, fish, amphipods, and mysids for their diet. As an oviparous species, they reproduce between February and June, occasionally breeding between October and January.[7]
References
Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Sebastes aleutianus". FishBase. June 2021 version.
"ScaleMaster Hall of Champions |". 27 October 2010.
Cailliet, G.M.; Andrews, A.H.; Burton, E.J.; Watters, D.L.; Kline, D.E.; Ferry-Graham, L.A. (2001). "Age determination and validation studies of marine fishes: do deep-dwellers live longer?". Experimental Gerontology. 36 (4–6): 739–764. doi:10.1016/S0531-5565(00)00239-4. PMID 11295512. S2CID 42894988.
Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Species in the genus Sebastes". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 1 November 2021.
James W. Orr and Sharon Hawkins (2008). "Species of the rougheye rockfish complex: resurrection of Sebastes melanostictus (Matsubara, 1934) and a redescription of Sebastes aleutianus (Jordan and Evermann, 1898) (Teleostei: Scorpaeniformes)". Fishery Bulletin. 106 (2): 111–134.
Christopher Scharpf & Kenneth J. Lazara, eds. (22 May 2021). "Order Perciformes (Part 8): Suborder Scorpaenoidei: Families Sebastidae, Setarchidae and Neosebastidae". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf and Kenneth J. Lazara. Retrieved 1 November 2021.
"Rougheye rockfish". Alaska Fisheries Science Center. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

