Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Cladus: Sarcopterygii
Classis: Dipnoi
Ordo: Lepidosireniformes
Familia: Protopteridae
Genus: Protopterus
Species: Protopterus annectens
Subspecies: P. a. annectens – P. a. brieni
Name
Protopterus annectens (Owen, 1839)
Type locality: Gambia River, western Africa.
Holotype (unique): RCSE uncat. (not found). Detailed description with figures appeared in Owen 1840. It is uncertain whether the holotype is/was deposited at RCSE or RCSHC.
Synonymy
Lepidosiren annectens Owen, 1839
Rhinocryptis annectens (Owen, 1839)
Protopterus anguilliformis Owen, 1841
Protopterus rhinocryptis Gray, 1850
Lepidosiren tobal Castelnau, 1855
Protopterus annectens brieni Poll, 1961
References
Primary references
Owen, R. 1839. On a new species of the genus Lepidosiren of Fitzinger and Natterer. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London 1839 [v. 1]: 27–32. BHL Reference page. [See pages 27, 32.]
Owen, R. 1840. Description of the Lepidosiren annectens. The Transactions of the Linnean Society of London v. 18 (pt 3) (art. 20): 327–361, Pls. 23–27. BHL Reference page.
Additional references
Johnels, A.G. & Svensson, G.S.O. 1954. On the biology of Protopterus annectens (Owen). Arkiv för Zoologi 7(7): 131–164. Reference page.
Links
Protopterus annectens – Taxon details on Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS).
Vernacular names
English: West African lungfish
中文: 原鰭魚
The West African lungfish (Protopterus annectens), also known as the Tana lungfish or simply African lungfish, is a species of African lungfish.[1][5] It is found in a wide range of freshwater habitats in West and Middle Africa, as well as the northern half of Southern Africa.[1][5]
Description
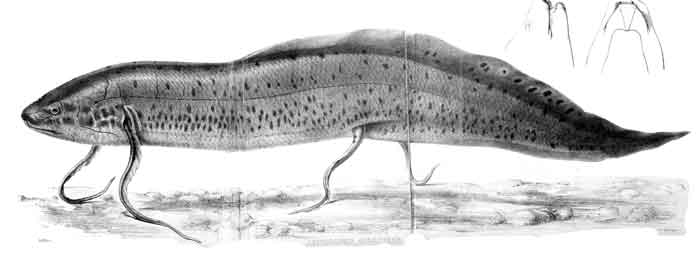
Protopterus annectens has a prominent snout and small eyes. Its body is long and eel-like, about 9–15 times the length of the head. It has two pairs of long, filamentous fins. The pectoral fins have a basal fringe and are about three times the head length, while its pelvic fins are about twice the head length. In general, three external gills are inserted posterior to the gill slits and above the pectoral fins.
It has cycloid scales embedded in the skin. About 40–50 scales occur between the operculum and the anus, and 36–40 around the body before the origin of the dorsal fin. It has 34–37 pairs of ribs. The dorsal side is olive or brown in color and the ventral side is lighter, with great blackish or brownish spots on the body and fins except on its belly.[6] West African lungfish can grow up to 1 meter long (3.3 feet) and weigh up to 4 kilograms (9 pounds).[7]
Distribution
The West African lungfish is distributed throughout Africa.[8] It has two subspecies; P. a. annectens is found primarily in the basins of Sahel as well as Guinea and Sierra Leone whilst the other subspecies, P. a. brieni is known largely from the upper Congo River area and from the Zambezi of Mozambique.[8]
Habitat
Like other African lungfish, the West African lungfish is an obligate air breather and a freshwater-dwelling fish.[8] It is demersal, meaning that it lives primarily buried within riverbeds. Due to the dry season frequently drying the rivers and floodplains in which it lives, the West African lungfish can aestivate for up to a year; however the West African lungfish generally only aestivates between wet seasons.[8]
Diet
The Tana lungfish has a diet not unlike other lungfish, consisting of various mollusks, crabs, prawn, and small fish within its distribution.[8] It can also go for up to 3+1⁄2 years without any food intake whatsoever. During this time period it behaves much like an aestivating fish in that it buries itself in the mud and does not move until more favorable conditions occur.[8]
When the African lungfish estivates, it burrows itself 12-18 inches deep into mud and as the mud dries, the mucus that envelops the fish forms a cocoon. The fish then has no direct contact with the outside environment; however, a tube of dried mucus goes into the pharynx of the fish and allows the fish to breathe. The fish usually relies on protein for energy, so the nitrogenous waste of amino acids is converted to urea, which builds up in the tissues and is only excreted when the lungfish returns to the water.[9]
References
Diouf, K.; Snoeks, J.; Lalèyè, P.; Contreras MacBeath, T. (2020). "Protopterus annectens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T169408A135027770. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T169408A135027770.en. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
ITIS.gov (Retrieved May 13, 2010.)
Haaramo, Mikko (2007). "Ceratodiformes – recent lungfishes". Mikko's Phylogeny Archive. Retrieved 3 July 2016.
Froese, R.; Pauly, D. (2017). "Protopteridae". FishBase version (02/2017). Retrieved 18 May 2017.
Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2014). "Protopterus annectens" in FishBase. April 2014 version.
"West African Lungfish | San Diego Zoo Animals & Plants". animals.sandiegozoo.org. Retrieved 2023-03-18.
"West African Lungfish". education.nationalgeographic.org. Retrieved 2023-05-16.
"Protopterus annectens summary page". FishBase. Archived from the original on 2022-01-25. Retrieved 2015-06-08.
Janssens, P. A. (1964). "The metabolism of the aestivating African lungfish". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. 11 (1): 105–117. doi:10.1016/0010-406X(64)90098-2. PMID 14170679.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

